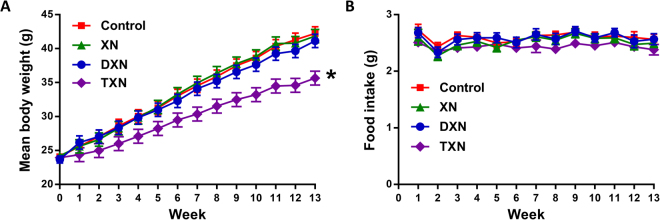
Xanthohumol (XN), a prenylated flavonoid from hops, improves dysfunctional glucose and lipid metabolism in animal models of metabolic syndrome (MetS). However, its metabolic transformation into the estrogenic metabolite, 8-prenylnaringenin (8-PN), poses a potential health concern for its use in humans. To address this concern, we evaluated two hydrogenated derivatives, α,β-dihydro-XN (DXN) and tetrahydro-XN (TXN), which showed negligible affinity for estrogen receptors α and β, and which cannot be metabolically converted into 8-PN. We compared their effects to those of XN by feeding C57BL/6J mice a high-fat diet (HFD) containing XN, DXN, or TXN for 13 weeks. DXN and TXN were present at higher concentrations than XN in plasma, liver and muscle. Mice administered XN, DXN or TXN showed improvements of impaired glucose tolerance compared to the controls. DXN and TXN treatment resulted in a decrease of HOMA-IR and plasma leptin. C2C12 embryonic muscle cells treated with DXN or TXN exhibited higher rates of uncoupled mitochondrial respiration compared to XN and the control. Finally, XN, DXN, or TXN treatment ameliorated HFD-induced deficits in spatial learning and memory. Taken together, DXN and TXN could ameliorate the neurocognitive-metabolic impairments associated with HFD-induced obesity without risk of liver injury and adverse estrogenic effects.