Recent Faculty Publication: Rad GTPase Deletion Attenuates Post-Ischemic Cardiac Dysfunction and Remodeling
Abstract
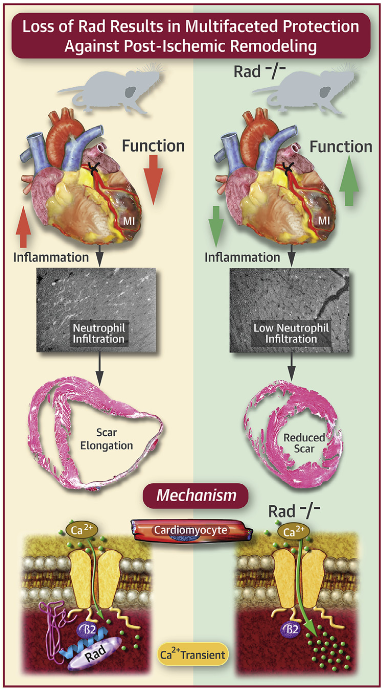
The protein Rad interacts with the L-type calcium channel complex to modulate trigger Ca2þ and hence to govern contractility. Reducing Rad levels increases cardiac output. Ablation of Rad also attenuated the inflammatory response following acute myocardial infarction. Future studies to target deletion of Rad in the heart could be conducted to establish a novel treatment paradigm whereby pathologically stressed hearts would be given safe, stable positive inotropic support without arrhythmias and without pathological structural remodeling. Future investigations will also focus on establishing inhibitors of Rad and testing the efficacy of Rad deletion in cardioprotection relative to the time of onset of acute myocardial infarction. (J Am Coll Cardiol Basic Trans Science 2018;3:83–96) © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier on behalf of the American College of Cardiology Foundation. This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (http://creativecommons. org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Saha Cardiovascular Research Center contributor, Dr. Ahmed Abdel-Latif
Janet R. Manning, PHD, Lakshman Chelvarajan, PHD, Bryana M. Levitan, BA, Catherine N. Withers, PHD, Prabhakara R. Nagareddy, PHD, Christopher M. Haggerty, PHD, Brandon K. Fornwalt, MD, PHD, Erhe Gao, MD, PHD, Himi Tripathi, PHD, Ahmed Abdel-Latif, MD, PHD, Douglas A. Andres, PHD, Jonathan Satin, PHD